ESG Report
Safety and Health

PPG is committed to operating safe and healthful workplaces
The most important PPG value is the safety and health of all employees. We seek to ensure that our employees and contractors return home safely each and every day by:
- Engaging with them to improve our operating practices around the world;
- Investing in a safe work environment; and
- Running our business with sound operating practices.
PPG seeks to market, distribute and manufacture products globally in a responsible manner that protects employees, neighbors, customers and the environment. To that end, our PPG EHS Process, our environmental health and safety management system, is integrated within each of our strategic business units and emphasizes our commitment to continuous improvement and sustainability. In addition, we prioritize integrating acquired businesses and facilities using a best practice EHS audit process.
In 2021, we implemented new training to make sure that our managers and operations leaders around the world were continually educated on process safety. We also spearheaded several new initiatives to standardize expectations for handling five-gallon pails, launched regional pilots for measuring progress of EHS culture and established a partnership with a thirdparty vendor to provide standardized EHS training content to implement globally. We also developed a new data visualization tool to more easily report and garner insights from EHS metrics that will help us implement ongoing process improvements.
We look to our environmental health and safety (EHS) policy and standards to define our expectations, and we implement programs and initiatives to reduce health and safety risks across PPG's business activities. To ensure progress against our goal of zero injuries, we strive to achieve an improvement of at least 5% per year in our injury and illness rate.
As a result of our efforts, we had no fatalities in 2021. In addition, by the end of 2021, we have realized an annual injury and illness reduction rate of 4.3% compared to the 2017 baseline.
The injury and illness rate for contractors was 0.17 in 2021, up from the 2020 rate of 0.15.
We continue to be diligent in our commitment to health and safety through effective management and tailor-made initiatives that respond to the various workplace environments of our global workforce.
Wuhu employees shoot for forklift safety, skills
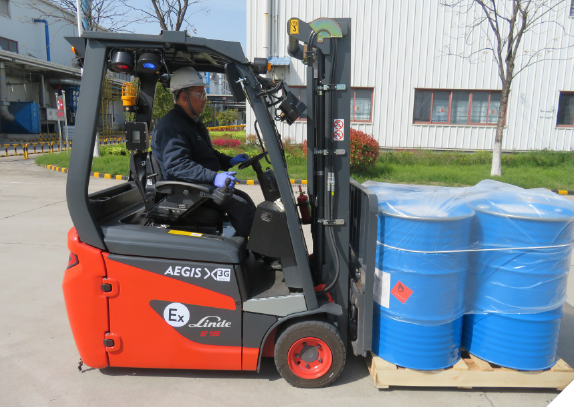 It's a given that the annual forklift skills competition at the coatings manufacturing plant in Wuhu, China, reinforces employee safety knowledge, improves driver skills and encourages more effective work. While 2021 marked the facility's seventh annual competition, there was a twist to test the mettle of the forklift drivers - a round of forklift basketball.
It's a given that the annual forklift skills competition at the coatings manufacturing plant in Wuhu, China, reinforces employee safety knowledge, improves driver skills and encourages more effective work. While 2021 marked the facility's seventh annual competition, there was a twist to test the mettle of the forklift drivers - a round of forklift basketball.
Eleven forklift drivers from the manufacturing plant enthusiastically took part in the half-day event. Drivers were able to showcase their skills in two acts: a written exam and on-site practice drills with the forklift. Other employees, including the warehouse manager, supervisors, coordinators, the EHS engineer and members of the plant's functional teams acted as judges. Through the written exam, which comprised 40% of the total score, participants could demonstrate their theoretical knowledge of topics such as safe forklift operation and forklift maintenance.
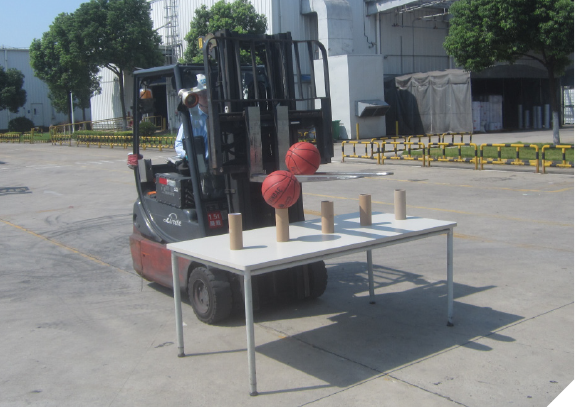 But the largest share of the score was awarded for displays of dexterity through two on-site activities:
But the largest share of the score was awarded for displays of dexterity through two on-site activities:
- Stacking and threading steel nuts on a thin steel strip on the forklift; and
- Dribbling and shooting basketballs with the forklift.
Driver Yun Yuanbao came out on top, scoring the highest number of total points to be named the site's 2021 forklift skills champion.
"These activities are designed to encourage employees to do better today than yesterday – everyday. That's The PPG Way."
Jerry Gu
Plant Manager, Wuhu
Health and Safety Management
We implement our EHS policy throughout our company globally using the PPG EHS management system, which we developed in accordance with Coatings Care, Responsible Care and ISO standards. The standardized principles and requirements established by our management system drive EHS integration into our purpose and business strategy. The system covers all people, including contractors who work at PPG-owned and -operated facilities, as well as PPG employees working in third-party facilities.
We hold an ISO14001/45001 integrated global certificate, which covers 55 sites. Many of our sites are also certified to the standard for their location-level management systems.
Our 12 EHS elements form the cornerstone of the management system and contain underlying principles and defined requirements.
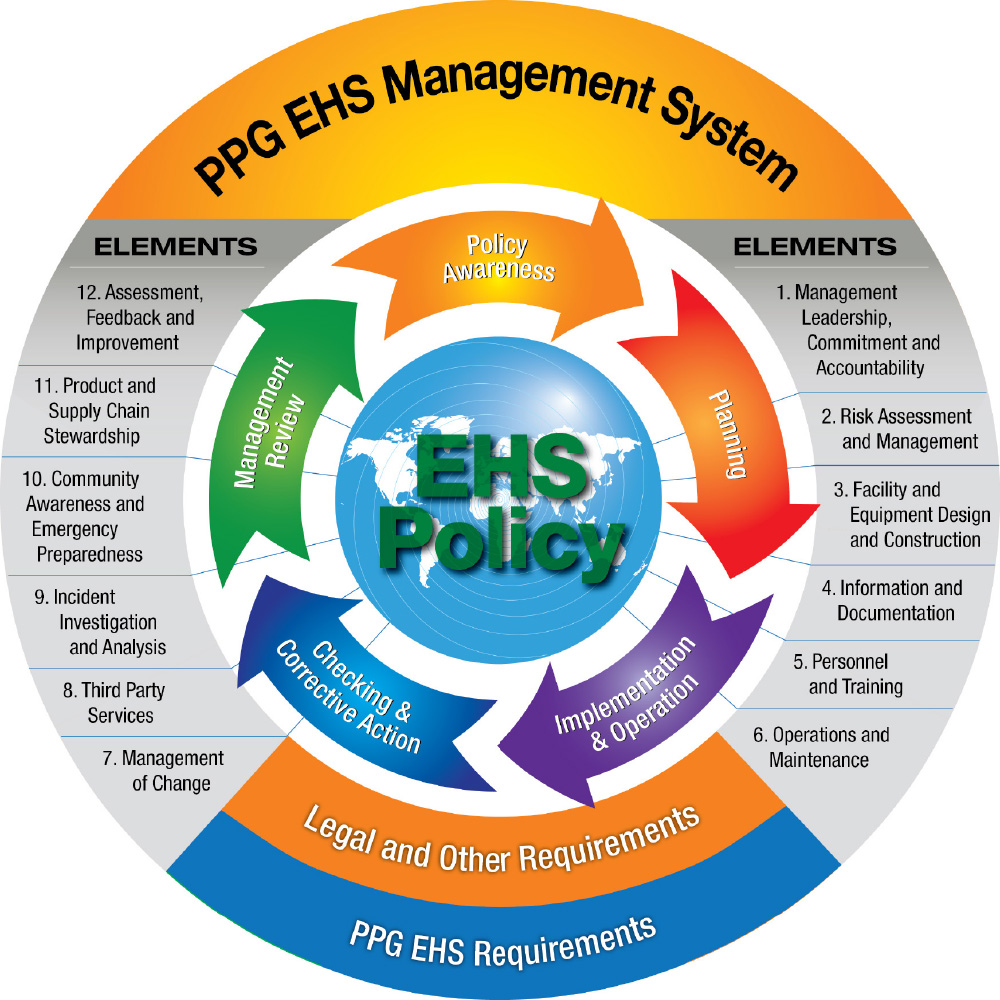
To ensure the requirements in our EHS management system remain effective at protecting our people and the environment, comply with current regulations and incorporate experiences within our facilities, we have established more than 70 topic teams. Each team focuses on a specific requirement, with an expectation for the team to meet at least two times a year.
An internal subject matter expert leads each topic team, which comprises permanent members from each region to maintain engagement with the site subject matter champions. Ad hoc members are added to develop and provide additional subject matter expertise.
Our EHS management system requires all of our locations to evaluate compliance with PPG and other requirements through assigned self-assessment tools and the completion of risk assessments, including job safety analyses, process hazard analyses and chemical risk assessments. These assessments must be conducted by experienced personnel, including experts outside of PPG, when appropriate.
When new facilities or companies join PPG through acquisition, we deploy a best practice compliance and integration process to ensure they align with and adopt PPG EHS standards and our EHS management system. Prior to the purchase of an acquisition, we begin a regimented, four-phase due diligence and integration process to evaluate the acquired company's EHS and product stewardship compliance practices as well as their EHS maturity. From the initial assessment and after the purchase, a detailed action plan is developed to address any deficiencies and implement PPG's EHS management system and related programs. The implementation of the action plan generally spans 24 months, with priority placed on regulatory compliance and key risk management topics. At the end of the 24-month period, the acquired operations undergo a corporate audit to validate the integration plan effectiveness and verify compliance with any identified regulatory gaps. After the first audit, new operations are incorporated into the corporate audit cycle based on their risk profile and historic EHS and product stewardship performance. As part of the acquisition integration and ongoing corporate audit process, we identify and monitor the need for capital expenditures to improve compliance and reduce risks to operations. Last year, we audited 12 acquired sites and invested $3.8 million to upgrade the facilities to meet these standards and ensure regulatory compliance for EHS matters.
In addition, we maintain an oversight audit plan conducted as part of our Corporate Compliance Assurance Program. Each of these efforts promotes a continuous improvement process to protect employees, neighbors, customers and the environment and to achieve mature EHS performance levels.
As part of our EHS management system, each of our locations has an active EHS leadership team that provides oversight, governs decisions and drives continuous improvement regarding the implementation of our EHS management system and other PPG and legal requirements. This team is expected to be led by top management, such as business leaders and the plant manager, and have cross-functional membership that includes the location’s leadership team, department representation and hourly employees. Ultimately, this team meets either on a monthly or quarterly basis to shape necessary plans and take required actions to realize our EHS policies and principles.
In addition, in 2021 we modified our internal organizational structure to establish EHS directors in all four major regions in which PPG operates. This reorganization ensures that our EHS approach is guided with a One PPG mentality. The regional directors, key business EHS directors and global directors, who are charged to continuously advance PPG's EHS expertise, report to our vice president of EHS, who has ultimate oversight.
Throughout 2021, we continued to develop and test new opportunities to improve PPG’s EHS culture through a series of regional pilots focused on measuring the maturity of the EHS culture at our sites. The pilots assessed our management system, with particular attention on the perception and engagement of employees at all levels in the process. The initial pilot was replicated across another region and is being refined for further implementation in 2022.
Our EHS management system also establishes a clear expectation that all employees actively participate in the implementation of the EHS management system and be engaged in the EHS implementation process, through interactions such as peer-to-peer observations and membership in focus teams that are dedicated to implementing or improving aspects of the EHS management system.
We continued developing standardized procedures for life-critical requirements in 2021. Our EHS data system includes a suite of modules to streamline the collection, tracking and dissemination of this critical information.
Cleveland and Barberton, Ohio, facilities receive safety awards from industry council
 Excellence in EHS practices come through big and small wins. Several recent examples can be seen in PPG facilities in Cleveland and Barberton, Ohio. These facilities recently received multiple Awards for Excellence from the Ohio Chemistry Technology Council (OCTC) for initiatives to eliminate spills and protect employee health.
Excellence in EHS practices come through big and small wins. Several recent examples can be seen in PPG facilities in Cleveland and Barberton, Ohio. These facilities recently received multiple Awards for Excellence from the Ohio Chemistry Technology Council (OCTC) for initiatives to eliminate spills and protect employee health.
The Barberton plant was honored for its "Walk the Line program," which requires team members to inspect every valve and connection before performing any of several procedures, including transferring material and returning equipment to service. Since implementation of this procedure in 2020, the plant has experienced an 84% reduction in significant spills and releases to secondary containment. Barberton also received an Award for Excellence in 2019.
The Cleveland facility received four OCTC Awards for Excellence for the following reasons:
- Elimination of injury risk by installing a pneumatic valve in place of a difficult-tooperate mechanical valve;
- 70% spill reduction in warehouse by relocating excess material to a more efficient site;
- Development of a pail holder to refill automated dispense tanks, reducing the potential for spills and risk of ergonomic and musculoskeletal injuries; and
- Improved disposal methods for small paint cans, which reduce hazardous waste volume, use of plastic, transportation expenses and disposal fees.
Preventing injury and illness
PPG tracks injuries and illnesses against our internal standard and U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration requirements. We also track against the ASTM E2920-19 record-keeping standard, which allows us to easily benchmark our performance against other companies. While our rate is fairly low compared to the majority of our benchmarked companies, we do have opportunities for improvement, specifically in the areas of slips, trips, falls and ergonomics.
We use a global electronic data management system for all EHS incidents. This system provides the tools to identify, report, record and investigate incidents, analyze root causes and trends, correct deficiencies and share and adopt relevant lessons learned.
Historically, motor vehicle accidents are one of our highest severity injury risks. We offer safe driver training and education programs to ensure our operations in every country have the tools and resources to manage this safety risk. All company vehicles have excellent crash ratings, and we invest in advanced safety features such as collision-avoidance systems and backup cameras. Learn more in the Transportation section.
Strains and sprains are another leading type of injury among our employees. Our focus on ergonomics includes training, monthly knowledge sharing and our annual PPG ERGO CUP® competition, which recognizes initiatives that minimize or eliminate ergonomic risks within our operations. Projects are submitted from all business units and functions across PPG globally. Top entries go on to compete in the Ergo Cup competition presented by the Institute of Industrial and System Engineers.
In 2021, our 17th annual internal Ergo Cup competition identified opportunities for PPG and our customers to save money and minimize risk of injuries through ergonomic ingenuity. We received more than 160 submissions. After a review by a global PPG team, we identified opportunities for injury prevention and financial savings for PPG and for customers. The HOMAX® TEX>>PRO™ sprayer system received the 17th annual Ergo Cup award for its lightweight design, which reduces weight up to 60% compared to traditional hopper spray guns.
Safety 365, which is our safety awareness and communications initiative, continued to empower our people to be safe and speak up if they see something that could be made safer. Each year, the program centers around a monthly safety theme that is supplemented with weekly tips which are reviewed at all levels of the organization for application regardless of location or activity.
We continued to implement human and organizational performance (HOP) at our locations during 2021, rolling out the program to eight more sites and training additional internal consultants to help drive implementation. We also conducted virtual bestpractice sharing sessions. At year’s end, more than 20 sites globally were using HOP to teach employees how to predict, prevent and manage errors that could result in injury.
Although the pandemic presented challenges with HOP implementation, we introduced HOP tools globally that included:
- A focus on high-risk tasks with a pre-task brief;
- Stop and seek out help as a tool when one is unsure;
- Three-part communication to increase our effectiveness;
- Procedure writing enhancements and step-by-step procedure adherence; and
- Verbalize, point and touch as a tool in conjunction with Walk the Line activities aimed at reducing spills and releases.
A HOP maturity matrix is incorporated into our standardized site scorecard. This scorecard includes both leading and lagging EHS indicators, and each site must use a risk prioritization tool annually to rank 80 EHS aspects and incorporate the top aspects into the new year’s scorecard and work plan.
To increase leadership engagement and dialogue about our health and safety efforts, our leaders are asked to ensure 20 measures are in place when visiting a site. These include traditional items such as clearly marked emergency exits, proper use of personal protective equipment and appropriate machine guarding. Other checklist items include safety awareness communications and the effective use of the standardized EHS management system site scorecard.
Our global EHS Advisory Council brings together talented young EHS professionals for development and engagement opportunities with their peers from around the world. In 2021, council members targeted establishing a global sustainable and standardized EHS/product stewardship training for all levels of management and supervision, with a focus toward line supervisors. A second project explored EHS/ product stewardship mentorship programs and aimed to standardize career planning tools for EHS/product stewardship professionals.
Global Health and Safety PerformanceEmployees and Supervised Workers |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fatalities |
PPG Injury and Illness Rate |
Total Recordable Incident Rate |
Lost Workday Rate |
Occupational Disease Rate |
||
|
2016 |
0 |
0 |
0.35 |
1.47 |
0.98 |
0.07 |
|
2017 |
0 |
0 |
0.31 |
1.26 |
0.90 |
0.05 |
|
2018 |
1 |
0.0019 |
0.27 |
1.25 |
0.85 |
0.09 |
|
2019 |
0 |
0 |
0.32 |
1.29 |
0.47 |
0.15 |
|
2020 |
0 |
0 |
0.26 |
0.99 |
0.37 |
0.12 |
|
2021 |
0 |
0 |
0.26 |
1.14 |
0.82 |
0.17 |
The fatality rate is the number of fatalities multiplied by 200,000 and divided by the number of work hours. A PPG injury and illness (I&I) is defined as an injury or illness that is significant enough that it is unlikely to go unreported, regardless of the reporting culture in the region or site. PPG I&Is include fatalities, fractures, surgeries, hospitalizations, 30 or more days of lost work and other similar criteria. The PPG I&I rate is the number of injuries and illnesses that meet this definition multiplied by 200,000 and divided by the number of work hours. Total recordable incident rate is the number of Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) recordable injuries multiplied by 200,000 and divided by the number of work hours. Lost workday rate is the number of injuries and illness that resulted in days away from work or restricted activity multiplied by 200,000 and divided by the number of work hours. Occupational disease rate is the number of illnesses multiplied by 200,000 and divided by the number of work hours.
2021 Health and Safety Performance by RegionEmployees and Supervised Workers |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fatalities |
PPG Injury and Illness Rate |
Total Recordable Incident Rate |
Lost Workday Rate |
Occupational Disease Rate |
|
|
Asia Pacific |
0 |
0.12 |
0.71 |
0.56 |
0.23 |
|
Europe, Middle East and Africa |
0 |
0.15 |
0.94 |
0.72 |
0.15 |
|
Latin America |
0 |
0.05 |
0.28 |
0.08 |
0.06 |
|
North America |
0 |
0.56 |
2.03 |
1.45 |
0.21 |
|
Global |
0 |
0.26 |
1.14 |
0.82 |
0.17 |
2021 Contractor Health and Safety Performance |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fatalities |
PPG Injury and Illness Rate |
Total Recordable Incident Rate |
Lost Workday Rate |
Occupational Disease Rate |
|
|
Asia Pacific |
0 |
0.00 |
0.13 |
0.13 |
0.00 |
|
Europe, Middle East and Africa |
0 |
0.22 |
0.89 |
0.45 |
0.00 |
|
Latin America |
0 |
0.49 |
1.62 |
0.49 |
0.00 |
|
North America |
0 |
0.43 |
1.51 |
0.43 |
0.00 |
|
Global |
0 |
0.17 |
0.76 |
0.31 |
0.00 |
Industrial Hygiene
PPG protects the health of our employees and supervised workers through our comprehensive industrial hygiene program, which has been in place for more than 50 years. The program centers on the anticipation, recognition, evaluation and control of long-term (chronic) and acute occupational health risks.
We employ credentialed toxicologists and industrial hygienists to oversee all aspects of our global program, and we continually improve it as knowledge of potential hazards and risk-control processes evolve.
We use formal processes to identify potential occupational health hazards by reviewing and analyzing information provided by suppliers of raw materials used in our manufacturing processes, as well as publicly available scientific literature. We also regularly review changes to published exposure limits from suppliers, governmental bodies and organizations, such as the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), to determine the basis for assessing exposure to chemical substances. We use exposure-limit changes and risk assessments of process tasks to define annual exposure monitoring plans for each manufacturing location.
Our manufacturing facilities are required to assess exposures to a defined list of substances and tasks where potential health risks are presented. We evaluate the results of these assessments to identify the need for improvements in manufacturing processes, facilities, training, personal protective equipment and medical surveillance.
We also work to eliminate substances of concern from our products and processes. Additional information can be found in the Product Stewardship section.
Our internal industrial hygiene laboratory analyzes air monitoring samples and is accredited by the American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA). We also use contract laboratories accredited by AIHA or applicable national governmental bodies. We maintain our exposure measurement results in a centralized data management system used by our operations teams globally. This system tracks our compliance with the annual sampling plans, results relative to applicable exposure limits and implementation of any corrective actions necessary to reduce exposures.
'Plant Hygiene CoE' offers best practices for clean production
Water and water-based raw materials can sometimes be the source of contamination such as fungi, mold or bacteria, but our new Plant Hygiene Center of Excellence (CoE) takes care of that.
A new CoE has been established in Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) to help PPG production facilities maintain high hygienic standards and meet growing regulatory requirements related to clean production.
The virtual CoE began as a 2017 project to help our Architectural Coatings (AC) facilities in EMEA prepare for a European Union legislative mandate requiring manufacturers to significantly reduce the amount of a specific preservative used during the production process. This led to a renewed focus on effective hygiene methods at PPG that could reduce contamination exposures and protect our AC products against bacteria or fungi.
Since then, the CoE team has worked with colleagues across 23 AC production sites in EMEA to develop and promote effective plant hygiene strategies. The Plant Hygiene Maturity Model, developed by PPG with support from an outside consultant, anchors these efforts and serves as a best practice to help PPG facilities improve and measure plant hygiene levels throughout the production process. The CoE team is also exploring rapid testing methods to check the quality of incoming raw materials in real-time.
We are currently exploring options to make our Plant Hygiene CoE a global effort.
Process Safety
Elements of process safety management are incorporated into PPG's global EHS Management System.
This approach provides a consistent set of requirements to all facilities globally in addition to any applicable regulatory requirements. The result is continuous improvement in safety, environmental performance and operational effectiveness. Our approach also benefits newly acquired facilities by allowing them to reach performance expectations more quickly.
In 2021, we had 0.04 tier one and 0.06 tier two process safety incidents per one million hours worked. We contained all of these incidents onsite without damage to the environment, and no permanent injuries were sustained. Per our process, we thoroughly investigated each incident to determine the root cause and ensure corrective actions were applied systematically and sustainably.
More than 67% of the 2021 incidents were primarily caused by equipment design or condition, which we resolved by redesigning processes, modifying maintenance methods or working with suppliers to improve equipment. A quarter of the incidents resulted from system-driven error, which we resolved by revising work methods, standardizing procedures and training all involved employees using HOP principles.
We further analyzed the incidents to identify common causes across businesses, such as whether they occurred while moving materials by truck, transferring materials by pipe or performing maintenance tasks. We used these data to develop improved methods and training to enhance and track performance. Our use of HOP continues to improve the interface between people and equipment to eliminate errors and other obstacles to effective performance.
We train our plant managers and operations directors globally to recognize the importance of a strong process safety culture and understand and abide by PPG's requirements for process safety.
These activities drive the mindset for process safety culture within facilities by helping teams understand why process safety should be incorporated into practices. Through trainings, managers also assess the process safety culture of their sites.
Our training courses offer pre-work and interactive in-class activities to understand regulatory standards, process safety management requirements and recognition and tools to sustain a healthy culture of process safety.
Customer Health and Safety
Our commitment to health and safety extends to our customers. Our products are not only manufactured safely in our facilities, but also transported, used and disposed of safely by our customers. Safe use and disposal instructions and safety data sheets are available for all products. Our product stewardship and technical experts are also available to provide one-on-one consultation on safe product use and disposal.
Process Safety PerformancePer Million Hours Worked |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Number of Tier One Incidents |
Tier One Incidents per Million Hours Worked |
Process Safety Total Incident Rate |
Process Safety Incident Severity Rate |
|
|
2019 |
23 |
0.20 |
0.04 |
0.02 |
|
2020 |
13 |
0.02 |
0.07 |
0.07 |
|
2021 |
5 |
0.04 |
0.06 |
0.09 |
Process safety total incident rate is the number of incidents multiplied by 1,000,000 and divided by the total annual hours worked by employees, contractors and subcontractors. Process safety incident severity rate is the total severity score for all process safety incidents multiplied by 1,000,000 and divided by the total annual hours worked by employees, contractors and subcontractors.
Process Safety Incidents |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Type of Event |
Root Cause |
Corrective Actions |
Tier Level |
|
Spill/Release during manufacturing process |
Equipment-corrosion, wear & tear |
Modify equipment design |
II |
|
Spill/Release during manufacturing process |
Equipment-corrosion, wear & tear |
Modify equipment design |
I |
|
Spill/Release during manufacturing process |
Equipment and pump failure |
Modify equipment design |
I |
|
Flash with property damage |
Equipment design/failure |
Modify equipment design, packaging process |
II |
|
Spill/Release during manufacturing process |
Human error |
Revise procedures and retrain |
II |
|
Spill/Release during manufacturing process |
Equipment design/failure |
Modify equipment design |
II |
|
Spill during movement of containers |
Personal medical event |
N/A |
II |
|
Chemical splash with injury |
Human error |
Contained; procedures revised |
I |
|
Chemical splash with injury |
Human error |
Contained; procedures revised |
I |
|
Spill/Release during manufacturing process |
Equipment-corrosion, wear & tear |
Contained; repaired pipe |
II |
|
Flash Fire with property damage |
Inadequate procedure |
Contained; procedures revised |
II |
|
Spill during manufacturing process |
Equipment-corrosion, wear & tear |
Contained; new global program developed to address deficiencies |
I |

